

1998 35(6):517–25.īasart H, Paes EC, Maas SM, van den Boogaard M-JH, van Hagen JM, Breugem CC, Cobben JM, Don Griot JPW, Lachmeijer AMA, Lichtenbelt KD, van Nunen DPF, van der Horst CM, Hennekan RC. Etiopathogenesis of isolated Robin sequence. Robin sequences and complexes: causal heterogeneity and pathogenetic/phenotypic variability. Underlying genetic diagnosis of Pierre Robin sequence: retrospective chart review at two children’s hospitals and a systematic literature review. Izumi K, Konczal LL, Mitchell AL, Jones MC. Robin sequence: a retrospective review of 115 patients.
#Collagenopathy with pierre robin sequence series
Pierre Robin sequence: a series of 117 consecutive cases. Holder-Espinasse M, Abadie V, Cormier-Daire V, Beyler C, Manach Y, Munnich A, Lyonnet S, Couly G, Amiel J. Brainstem dysfunction: a possible neuroembryological pathogenesis of isolated Pierre Robin sequence. 2015 167A:1972–82.Ībadie V, Morisseau-Durand MP, Beyler C, Manach Y, Couly G. Birth prevalence of Robin sequence in the Netherlands from 2000–2010: a retrospective population-based study in a large Dutch cohort and review of the literature. Paes EC, van Nunen DPF, Basart H, Don Griot JPW, van Hagen JM, van der Horst CMAM, van den Boogaard M-JH, Breugem CC. Pierre Robin sequence: appearances and 25 years of experience with an innovative treatment protocol. Clinical consensus report: diagnosis and evaluation of infants with Robin sequence. 1983 36(4):434–7.īreugem CC, Evans KN, Poets CF, Suri S, Picard A, Filip C, Paes EC, Mehendale FV, Saal HM, Basart H, Murthy J, Joosten KFM, Speleman L, Collares MVM, van den Boogaard MJ, Muradin M, Andersson ME, Kogo M, Farlie PG, Don Griot P, Mossey PA, Slator R, Abadie V, Hong P. Incidence of the Robin anomalad (Pierre Robin syndrome). Pierre Robin sequence in Denmark: a retrospective population-based epidemiological study. Robin sequence: clearing nosologic confusion. Will the right Robin patient rise, please? Definitions and criteria during management of Robin sequence patients in the Netherlands and Belgium. 2009 62(12):1555–8.īasart H, Kruisinga FH, Breugem CC, Don Griot JP, Hennekam RC, Van der Horst CM. What is ‘Pierre Robin sequence’? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.

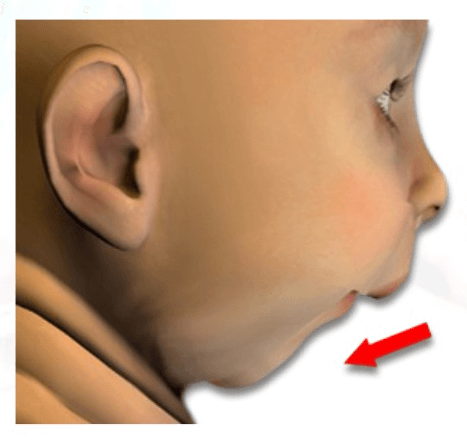
Glossoptosis due to atresia and hypotrophy of the mandible. A fall of the base of the tongue considered as a new cause of nasopharyngeal respiratory impairment: Pierre Robin sequence, a translation-1923. La chute de la base de la langue consideree comme une nouvelle cause de gene dans la respiration nasopharyngienne. Subperiosteal release of the floor of the mouth to correct airway obstruction in Pierre Robin sequence: review of 31 cases. The Pierre Robin sequence: review of 125 cases and evolution of treatment modalities. KeywordsĬaouette-Laberge L, Bayet B, Larocque Y. This chapter describes the condition, and outlines management options and outcomes. Investigation and management regimes vary widely, but the specific definitions of PRS used in published literature are numerous making comparison between treatments difficult.Recently a consensus document has been published, the aim of which is to improve consistency in definition of PRS and thus improve the evidence base for intervention. Pierre Robin Sequence (PRS) is a rare condition described in the early twentieth century as the triad of micrognathia, glossoptosis and upper airway obstruction occurring in infants.Up to 90% of infants affected will have a cleft palate.The severity of the condition varies widely.The airway obstruction may be immediately life threatening, or associated with difficulties with feeding and faltering growth which can also be severe.More commonly the airway obstruction is more mild, and can often be managed by conservative intervention such as positioning of the child.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
